Understanding the Components of MIG Welding Torches: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Components of MIG Welding Torches: A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to MIG Welding Torches
2. What is MIG Welding?
3. Overview of MIG Welding Torch Components
4. The Torch Body: Structure and Function
5. The Contact Tip: The Heart of the Torch
6. The Nozzle: Focusing the Arc
7. The Liner: Guiding the Filler Material
8. The P
Understanding the Components of MIG Welding Torches: A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to MIG Welding Torches
- 2. What is MIG Welding?
- 3. Overview of MIG Welding Torch Components
- 4. The Torch Body: Structure and Function
- 5. The Contact Tip: The Heart of the Torch
- 6. The Nozzle: Focusing the Arc
- 7. The Liner: Guiding the Filler Material
- 8. The Power Cable: Delivering Energy to the Torch
- 9. The Trigger: Controlling the Welding Flow
- 10. Conclusion
- 11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Introduction to MIG Welding Torches
MIG welding, or Metal Inert Gas welding, is a popular fabrication process widely used in various industries. The efficiency and versatility of MIG welding largely depend on the performance of its key tool—the MIG welding torch. Understanding the components of MIG welding torches is crucial for both novice and experienced welders. In this article, we will delve deep into the essential parts of these torches, elucidating their functions and importance in achieving high-quality welds.
2. What is MIG Welding?
MIG welding is a semi-automatic or automatic arc welding process that uses a continuous feed of filler material to join metals. It employs a shielding gas to protect the weld pool from atmospheric contamination. This process is renowned for its speed, ease of use, and ability to weld a variety of metals, including steel, aluminum, and stainless steel. The MIG welding torch plays a pivotal role in ensuring the effectiveness of this process.
3. Overview of MIG Welding Torch Components
A MIG welding torch comprises several key components that work together to produce a clean, strong weld. Each part has a specific function that contributes to the overall welding process. The primary components include:
- The torch body
- The contact tip
- The nozzle
- The liner
- The power cable
- The trigger
This article will explore each component in detail to provide a clear understanding of their roles and importance.
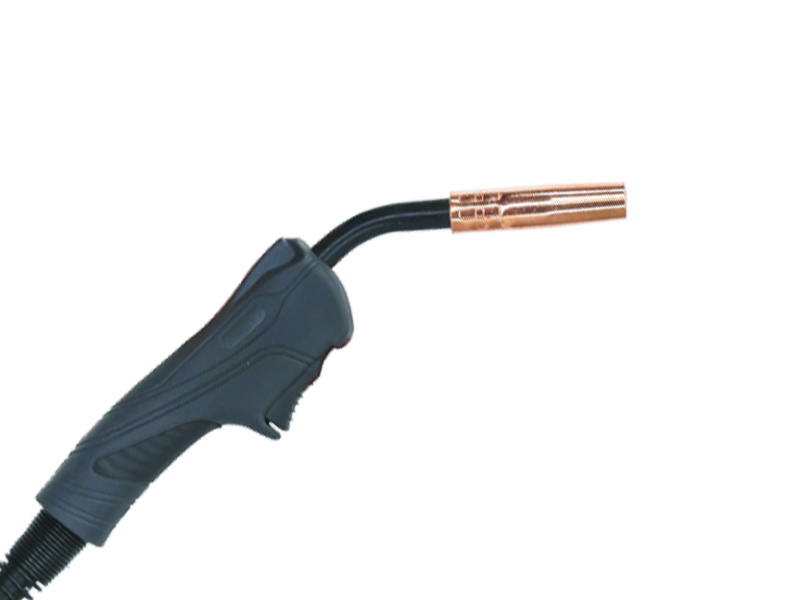
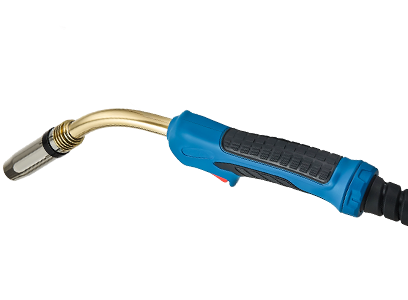
4. The Torch Body: Structure and Function
The **torch body** is the main structure of the MIG welding torch, housing all the internal components. It is typically made from durable materials such as aluminum or plastic, designed to withstand high temperatures and resist electrical conductivity. The design of the torch body allows for comfortable handling and maneuverability, essential for achieving precise welds.
The torch body also contains a gas channel that directs the shielding gas towards the weld pool, helping to protect it from oxidation. The ergonomic design of modern torch bodies often includes grips that reduce fatigue during prolonged welding sessions.
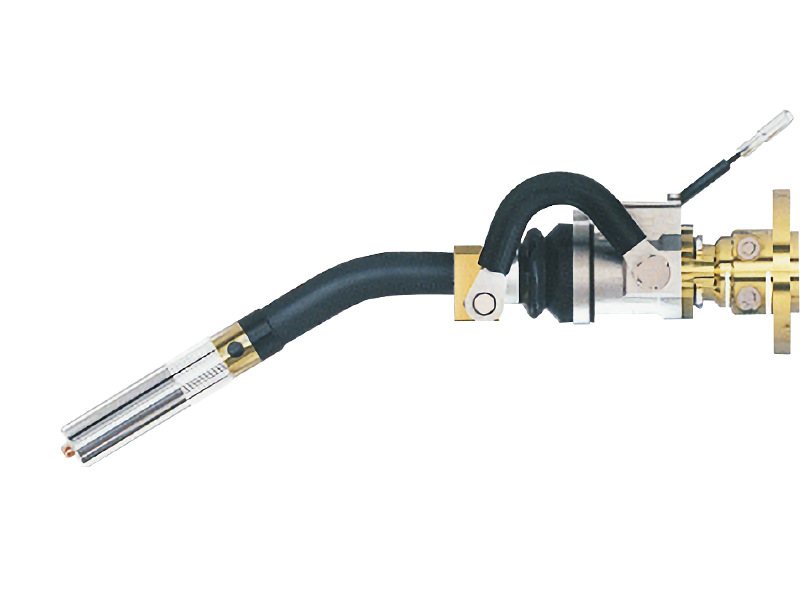
5. The Contact Tip: The Heart of the Torch
The **contact tip** is perhaps the most critical component of a MIG welding torch. It is where the electrical arc is established between the tip and the workpiece. The contact tip is designed to fit over the electrode and is typically made from copper due to its excellent electrical conductivity.
The contact tip has a specific diameter that correlates with the size of the filler wire being used. A properly sized contact tip ensures a consistent arc and prevents issues such as poor penetration or spatter. Regular inspection and replacement of the contact tip are essential, as wear can lead to an unstable arc and compromised weld integrity.
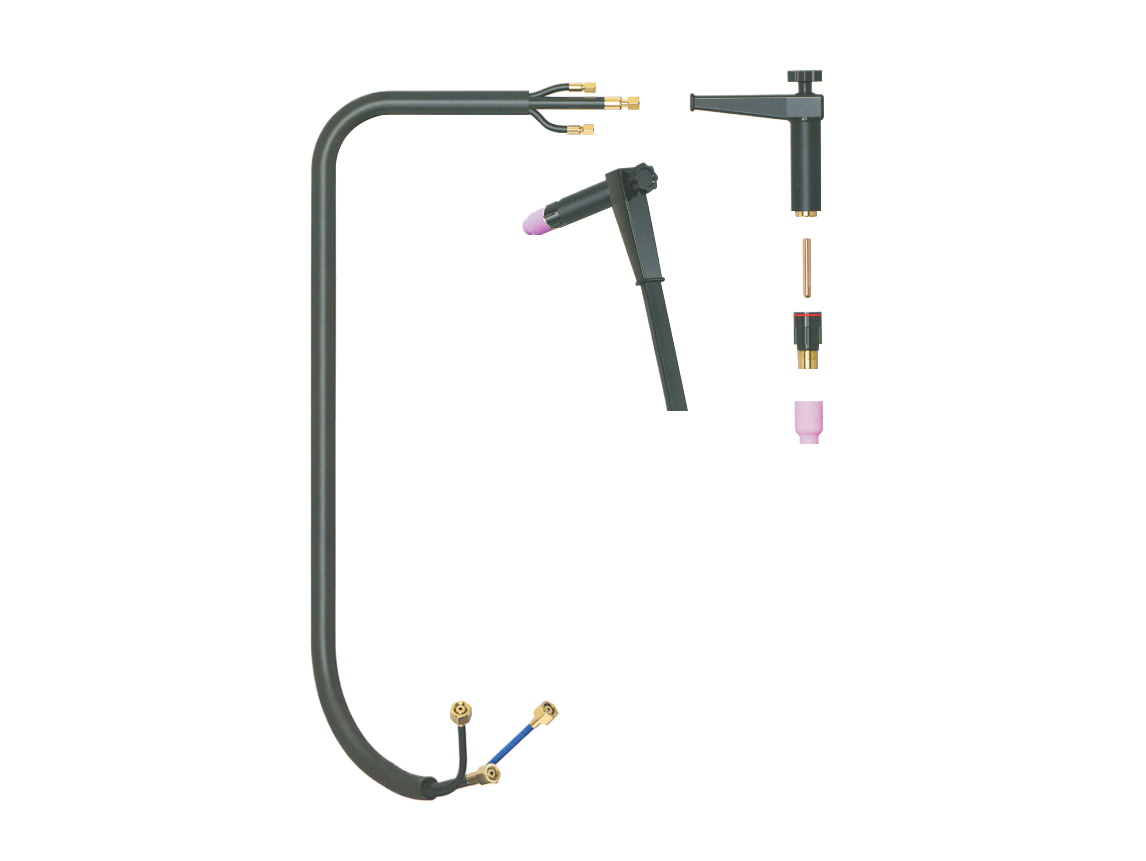
6. The Nozzle: Focusing the Arc
The **nozzle** serves as a protective covering for the contact tip and plays a crucial role in directing the shielding gas around the weld area. Available in various sizes and shapes, the nozzle can significantly affect the quality of the weld.
Nozzles are typically made from ceramic or copper, materials that can withstand high temperatures. The correct nozzle size is essential; too large of a nozzle can lead to inefficient gas shielding, while a nozzle that is too small might not provide adequate protection, risking contamination of the weld pool.
7. The Liner: Guiding the Filler Material
The **liner** is an internal component of the MIG welding torch that guides the filler wire from the spool to the contact tip. Made of materials like nylon or Teflon, the liner must maintain a smooth surface to prevent friction and ensure a consistent feed of the welding wire.
A well-maintained liner is vital for smooth wire feeding, reducing the chances of wire jams or feed issues. Different welding applications may require different liner types, and regular inspection is essential to maintain optimal performance.
8. The Power Cable: Delivering Energy to the Torch
The **power cable** connects the MIG welding torch to the welding machine, delivering the necessary electrical current for the welding process. Typically insulated and flexible, the power cable must withstand high temperatures and mechanical wear due to constant movement during welding.
Choosing the right gauge of wire for the power cable is crucial, as inadequate power supply can lead to poor arc stability and inconsistent weld quality. Regular checks for wear or damage to the power cable help ensure safe and efficient operation.
9. The Trigger: Controlling the Welding Flow
The **trigger** is the control mechanism of the MIG welding torch, allowing the welder to start and stop the welding process at will. It is typically located on the torch handle for easy access.
Modern MIG torches may feature various trigger options, including standard triggers, which require a simple pull, and more advanced options like trigger locks for continuous welding. The trigger's responsiveness and ergonomics are essential for comfortable and efficient welding, especially during extended use.
10. Conclusion
Understanding the components of MIG welding torches is essential for anyone involved in the welding industry. Each part, from the torch body to the contact tip, plays a unique role in ensuring high-quality welds. Knowledge of these components not only aids in selecting the right equipment but also in performing maintenance and troubleshooting issues that may arise during welding projects.
By gaining a deeper understanding of MIG welding torches, welders can enhance their skills, optimize their equipment, and ultimately produce superior welds that meet industry standards.
11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the purpose of the shielding gas in MIG welding?
The shielding gas protects the weld pool from atmospheric contamination, which can lead to defects such as porosity and oxidation. Common shielding gases include argon, helium, and carbon dioxide.
2. How often should I replace the contact tip?
The contact tip should be inspected regularly for wear. It is advisable to replace it when you notice signs of wear or when you experience arc stability issues, typically every few hours of use.
3. Can I use different sizes of nozzles with the same MIG welder?
Yes, you can use different nozzle sizes depending on the application and thickness of the material being welded. However, ensure that the nozzle is compatible with your specific contact tip and welding wire size.
4. What materials can I weld using a MIG welding torch?
MIG welding torches are versatile and can be used to weld a variety of materials, including mild steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. The choice of filler wire and shielding gas will depend on the material being welded.
5. How do I maintain my MIG welding torch for optimal performance?
Regular maintenance involves checking and replacing worn components such as the contact tip and liner, cleaning the nozzle, and ensuring the power cable is in good condition. It helps maintain consistent performance and prolongs the life of the torch.
By addressing these FAQs, we aim to provide further clarity and assist welders in optimizing their use of MIG welding torches and enhancing their welding experience.
TAG:
Previous:
Related Posts
Understanding the Components of MIG Welding Torches: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Components of MIG Welding Torches: A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to MIG Welding Torches
2. What is MIG Welding?
3. Overview of MIG Welding Torch Components
4. The Torch Body: Structure and Function
5. The Contact Tip: The Heart of the Torch
6. The Nozzle: Focusing the Arc
7. The Liner: Guiding the Filler Material
8. The P