Mastering the Technique: How to Use MIG Welding Torches Effectively
Mastering the Technique: How to Use MIG Welding Torches Effectively
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to MIG Welding and Its Importance
2. Understanding MIG Welding Torches
3. Components of a MIG Welding Torch
4. Prepping Your Workspace for MIG Welding
5. Setting Up the MIG Welding Torch Correctly
6. Essential MIG Welding Techniques and Tips
7. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Mastering the Technique: How to Use MIG Welding Torches Effectively
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to MIG Welding and Its Importance
- 2. Understanding MIG Welding Torches
- 3. Components of a MIG Welding Torch
- 4. Prepping Your Workspace for MIG Welding
- 5. Setting Up the MIG Welding Torch Correctly
- 6. Essential MIG Welding Techniques and Tips
- 7. Common Mistakes to Avoid in MIG Welding
- 8. Maintenance and Care for MIG Welding Torches
- 9. Conclusion
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions
1. Introduction to MIG Welding and Its Importance
MIG welding, or Metal Inert Gas welding, has become a cornerstone in the welding industry due to its versatility and efficiency. This process uses a continuous wire feed to create a weld pool that joins two pieces of metal. Understanding how to effectively use MIG welding torches can significantly enhance your welding skills, improve productivity, and ensure high-quality results. In this article, we delve into the intricate details of using MIG welding torches, providing insights that every welder, from beginner to expert, can leverage.
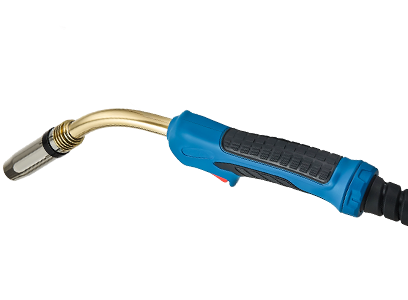
2. Understanding MIG Welding Torches
MIG welding torches are vital tools that facilitate the welding process by delivering filler material and shielding gas to the weld area. They come in various types, each designed for specific applications and user comfort. Knowing the different kinds of MIG welding torches and their specific uses can help you make informed decisions on which one to use for your projects.
Types of MIG Welding Torches
There are primarily two types of MIG welding torches: air-cooled and water-cooled torches.
- **Air-Cooled Torches**: These are lightweight and easy to handle, making them ideal for short welding tasks or hobbyist projects. They rely on airflow to dissipate heat.
- **Water-Cooled Torches**: Designed for prolonged use, water-cooled torches can handle higher amperages and are more efficient for heavy-duty welding jobs. They circulate water around the torch to keep it cool.
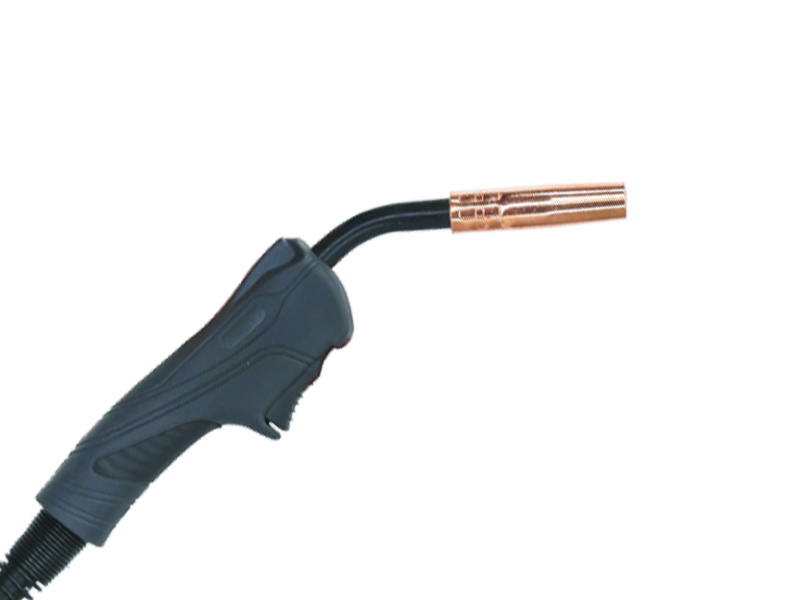
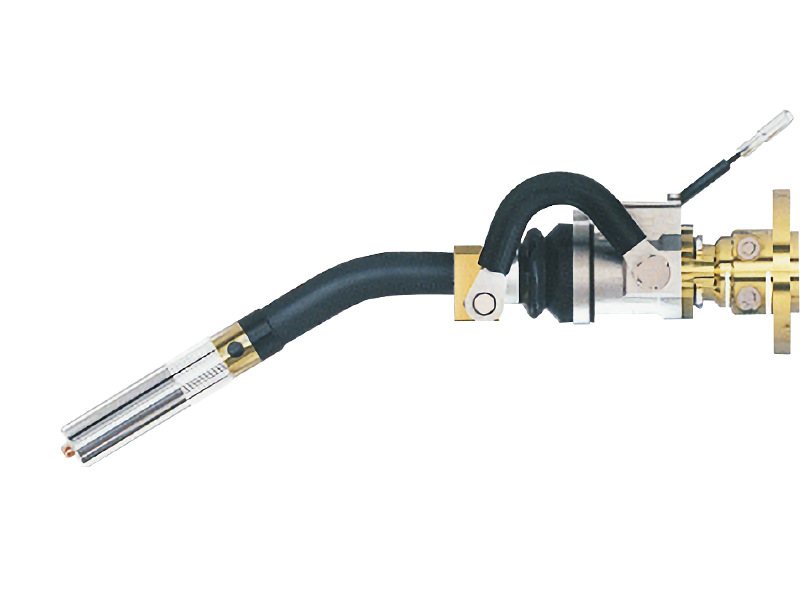
3. Components of a MIG Welding Torch
A MIG welding torch consists of several key components, each playing a crucial role in the welding process.
The Gun
The gun is the most recognizable part of the torch. It houses the wire feed mechanism and delivers the welding wire to the workpiece.
Contact Tip
The contact tip is where the welding wire exits the torch. It ensures electrical conductivity and must be compatible with the diameter of the welding wire you are using.
Gas Nozzle
The gas nozzle protects the weld pool from contamination by shielding gas. Proper selection and maintenance of the nozzle are vital for achieving a clean weld.
Collet and Collet Body
These components secure the contact tip in place and allow for adjustments, ensuring the correct alignment of the wire and the workpiece.
4. Prepping Your Workspace for MIG Welding
A well-organized workspace is essential for effective MIG welding. Here are several steps to prepare your area:
Safety First
Ensure that you have the appropriate safety gear, including gloves, helmets, and protective clothing.
Clean the Work Area
Remove any flammable materials from your workspace. Oil, dust, and debris can lead to dangerous situations when welding.
Setting Up Your Equipment
Organize your tools and materials within reach. Make sure your MIG welding machine and torches are positioned for optimal efficiency.
5. Setting Up the MIG Welding Torch Correctly
Setting up your MIG welding torch correctly is paramount for achieving the best results.
Wire Feed Setting
Adjust the wire feed speed according to the thickness of the materials you are welding. This setting can vary based on the type of wire and the welding process.
Gas Flow Rate
Set the gas flow rate based on the manufacturer's recommendations. Typically, a flow rate of 15-25 cubic feet per hour (CFH) is standard.
Voltage and Amperage Settings
Set the voltage and amperage according to the material properties and thickness. Consult the welding machine’s manual for optimal settings.
6. Essential MIG Welding Techniques and Tips
Mastering MIG welding involves more than simply knowing how to use the torch. Here are some techniques and tips to enhance your skills:
The Push vs. Pull Technique
Using the push technique involves moving the torch away from the weld pool, while the pull technique means moving it towards the weld pool. Each technique has distinct benefits, with the push technique generally providing a cleaner weld.
Travel Speed
Maintaining a consistent travel speed is crucial. Too fast can lead to weak welds, while too slow can cause burn-through or excessive spatter.
Angle of the Torch
Hold the torch at a slight angle (around 10-15 degrees) to optimize gas coverage and ensure a stronger arc.
7. Common Mistakes to Avoid in MIG Welding
Even experienced welders can fall into traps that lead to poor results. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
Inconsistent Wire Feed
A fluctuating wire feed can lead to inconsistent welds. Regularly check and adjust the feed to maintain stability.
Improper Gas Coverage
Inadequate shielding gas coverage can lead to contamination. Ensure that your gas nozzle is clean and that you are using the correct gas mixture for your materials.
Neglecting Equipment Maintenance
Regularly inspect and maintain your MIG welding torch and equipment. Worn-out tips or improperly set gas flow can significantly impact the quality of your welds.
8. Maintenance and Care for MIG Welding Torches
Proper maintenance ensures the longevity and efficiency of MIG welding torches.
Cleaning the Torch
After each use, clean the nozzle and contact tip to prevent build-up that can hinder performance.
Regular Inspection
Check the hose connections, cable integrity, and electrical components for damage. Replace any worn or damaged parts promptly.
Storing Your Equipment
Store your MIG welding torch in a dry, cool place to prevent rust and corrosion. Protect the tips and nozzles to keep them in optimal condition.
9. Conclusion
Mastering the use of MIG welding torches is essential for anyone looking to improve their welding skills and achieve high-quality results. By understanding the components, setting up your equipment correctly, employing proper techniques, and maintaining your tools, you can enhance your welding performance significantly. With practice and adherence to these guidelines, you’ll be on your way to becoming a proficient MIG welder.
10. Frequently Asked Questions
1. What type of gas is required for MIG welding?
For MIG welding, a mixture of argon and carbon dioxide is commonly used. Pure argon is suitable for welding non-ferrous metals.
2. How do I choose the right diameter of welding wire?
The diameter of the welding wire should match the thickness of the materials being welded. For thin materials, use a smaller diameter wire, while thicker materials require larger diameters.
3. Can I use MIG welding for outdoor projects?
Yes, but it’s essential to protect the weld area from wind to ensure proper gas coverage. Using a windbreak or welding in a sheltered area can help.
4. How often should I change the contact tip?
Change the contact tip when you notice excessive spatter, reduced wire feed efficiency, or if it appears worn or damaged.
5. What is the best technique for beginners in MIG welding?
Beginners should start with the push technique while maintaining a steady travel speed and consistent angle. Practicing on scrap metal helps build confidence and skill.
By following these guidelines and continually practicing, you can master the technique of using MIG welding torches effectively, setting yourself up for success in all your welding projects.
TAG:
Related Posts
Essential Insights on MIG Torch Replacement: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, the torch is one of the most vital components of the entire setup. Over time, as with any tool or equipment, MIG torches can wear out or become damaged, necessitating a replacement to maintain welding quality and efficiency. Understanding the nuances of MIG torch replacement can make a significant difference in your welding outcomes.
First and foremo